There’s a growing recognition of the importance of making your website accessible to everyone, including those with disabilities. By implementing practical strategies, you can create an inclusive online environment that enhances user experience and broadens your audience. This guide will walk you through crucial steps that you can take to improve your website’s accessibility, ensuring that all visitors can navigate and benefit from your content effortlessly.
Key Takeaways:
- Alternative Text: Use descriptive alt text for images to ensure visually impaired users can understand the content through screen readers.
- Keyboard Navigation: Ensure that all interactive elements are accessible via keyboard, allowing users who cannot use a mouse to navigate your site easily.
- Color Contrast: Maintain high color contrast between text and background to enhance readability for users with visual impairments.
Understanding Website Accessibility
What is Website Accessibility?
The term “website accessibility” refers to the practice of ensuring that all users, regardless of their abilities or disabilities, can effectively access and interact with your website. This includes individuals with visual, auditory, motor, and cognitive impairments.
You want to provide a digital experience that allows everyone to navigate your content, engage with your services, and participate fully in the functionalities your site offers. Accessibility encompasses a variety of elements, including text alternatives for images, easy navigation, and compatibility with assistive technologies like screen readers.
Some common practices that enhance website accessibility involve using semantic HTML, providing accessible forms, and ensuring adequate contrast between text and background colors. By adhering to established guidelines, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), you can improve the usability of your website for all users. This not only allows people with disabilities to access your services but can also enhance the overall user experience for everyone who visits your site.
Importance of Accessibility in Digital Content
Any effort you make to improve accessibility isn’t solely about compliance with legal standards; it’s about inclusivity and ensuring that you’re reaching the widest possible audience. Accessible digital content means that people with disabilities can access information and services just like anyone else, allowing them to participate fully in your online community. Additionally, search engines often favor accessible websites, potentially boosting your search engine rankings and increasing visibility among all users.
Website accessibility impacts not just the user experience for individuals with disabilities but can also enhance usability for all visitors. Streamlined navigation and clear content presentation make it easier for everyone, regardless of their circumstances, to find the information they need swiftly.
Moreover, fostering an inclusive environment strengthens your brand’s reputation and can translate into a broader audience and higher customer satisfaction. Investing in accessibility is not just a responsibility; it’s a smart business decision that invites diversity and maximizes your reach.
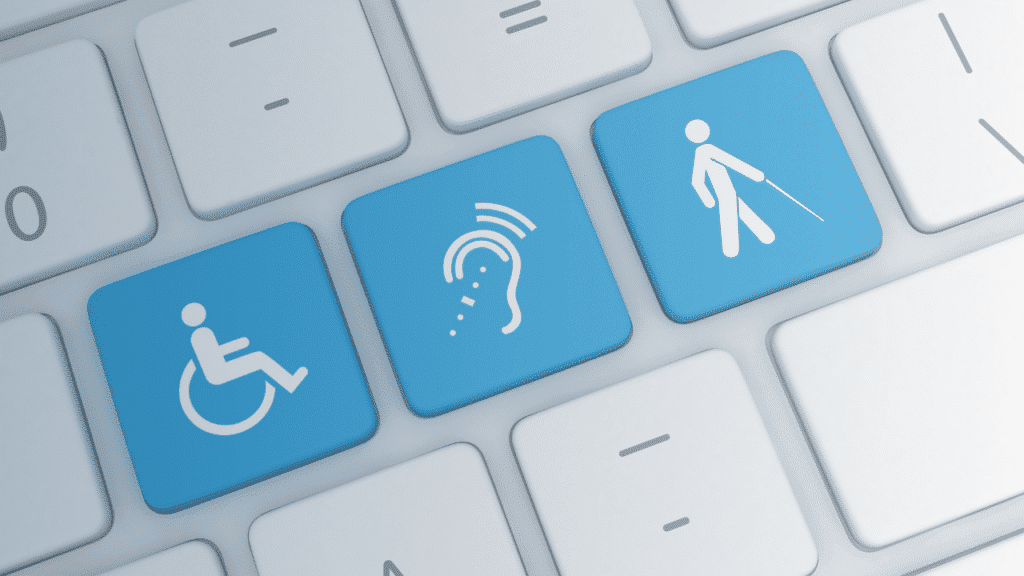

Key Factors to Consider
You must consider various factors to enhance your website’s accessibility effectively. Start by evaluating your site’s navigational structure and overall layout. Ensure that all interactive elements are keyboard accessible and that your content is structured in a way that promotes easy reading. Additional considerations include:
- Use of proper headings and semantic HTML tags
- Providing alt text for images
- Setting a high contrast between text and background colors
- Ensuring that forms are properly labeled
- Offering captions and transcripts for multimedia content
This holistic approach will significantly contribute to a more accessible web experience. For more detailed information, check out Web Accessibility: The Ultimate Guide.
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
Clearly, the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) provide a comprehensive framework for making web content more accessible to individuals with disabilities. These guidelines outline various principles, such as perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust (POUR), forming the backbone of web accessibility best practices. Each of these principles encompasses specific criteria that should be met to ensure your website serves all users effectively.
When adhering to WCAG standards, you can significantly increase the usability of your website for those with varying abilities. These guidelines not only assist individuals who are visually impaired or hard of hearing but also those who may have cognitive disabilities. By following WCAG, your website will not only become more inclusive but also boost your overall user experience.
Inclusivity for Diverse Users
WCAG standards play a vital role in promoting inclusivity for diverse users. They support various assistive technologies that individuals with disabilities may rely on to navigate the web effectively. By applying these guidelines, you can remove barriers that might prevent users from accessing your content or services.
Accessibility is about creating an environment where all users can interact with your site seamlessly. This includes ensuring screen reader compatibility, alt texts for images, and consistent navigation that can be understood and used by users with various cognitive and physical abilities. By prioritizing inclusivity, you not only comply with legal requirements but also foster a welcoming online experience for everyone.
How to Audit Your Website for Accessibility
Not every website passes accessibility standards, and evaluating your site is imperative for ensuring inclusivity for all users. Conducting an audit involves both automated and manual processes that will help identify areas where your website can improve. You can utilize various tools and techniques to assess the accessibility of your content, design, and functionality, ultimately creating a more welcoming online environment for everyone.
Tools for Accessibility Testing
Assuming you have an understanding of web accessibility standards, there are several automated tools available that can streamline the testing process. A combination of tools such as WAVE, Axe, and Lighthouse can help you identify issues such as color contrast, missing alt text, and improper heading structures. While these tools can quickly uncover many accessibility issues, it’s important to supplement automated testing with manual inspections to ensure comprehensive coverage.
Conducting User Testing
To enhance your website’s accessibility, conducting user testing with real individuals who have disabilities is invaluable. This process involves gathering a diverse group of users who navigate your website under various circumstances, such as using screen readers or voice commands. Their feedback will provide insight into the practical challenges they face while navigating your site, ultimately allowing you to address specific pain points others may encounter.
With user testing, you can gain firsthand perspectives on how accessible your website truly is. By observing participants as they interact with your site, you can pinpoint areas that may require adjustments or redesign. Furthermore, involving users with disabilities in the testing process fosters authentic relationships and ensures your website can cater to the needs of all visitors effectively. Experience gained from user testing will guide you in making informed decisions toward an inclusive design strategy.
Tips for Improving Website Accessibility
For anyone tasked with enhancing their website’s accessibility, several key strategies can be beneficial. Begin by evaluating your site and prioritizing these improvements to ensure a more inclusive experience for all users. Here are a few tips to consider:
- Utilize clear, simple language for better understanding.
- Ensure proper color contrast between text and background.
- Implement headers and lists for better content structure.
- Add descriptive alt text for images and non-text content.
- Make sure links are easily identifiable and descriptive.
The information you provide can significantly impact the accessibility of your website. For a deeper investigate comprehensive strategies, check out 11 Important Ways To Make Your Website Accessible.
Text Alternatives for Non-Text Content
The inclusion of text alternatives for non-text content is vital for making your website accessible to users with visual impairments. Each image, video, or other non-text media should have descriptive alt text that conveys the purpose or content. This practice not only assists individuals using screen readers but also ensures that important information is not lost. Alt text should be descriptive enough to provide context but concise enough to be easily read and understood.
The implementation of proper text alternatives goes beyond just images; audio and video content should also have transcripts and captions. This will allow users with hearing impairments to access auditory content, thus creating a more complete and engaging experience for all visitors to your site.
Designing for Keyboard Navigation
The ability to navigate your website using only a keyboard is a key aspect of accessibility. Many users rely on keyboard navigation due to physical disabilities that make mouse usage difficult. To facilitate this, ensure that all interactive elements, such as links, buttons, and forms, can be accessed and activated using keyboard commands. A visible focus style for elements is also imperative to make it clear which item is currently selected during keyboard navigation.
With the right design practices, you can create a site that is easily navigable for keyboard users. This includes providing a logical tab order and utilizing elements like skip links that allow users to bypass repetitive navigation menus. Taking the time to optimize for keyboard navigation will result in a smoother and more inclusive browsing experience for all your audience.
Enhancing Visual Accessibility
To improve visual accessibility on your website, you need to prioritize features that cater to various levels of visual ability. This means considering elements like color contrast, font choices, and responsive design, ensuring that your content is readable and appealing to all users. By implementing thoughtful design strategies, you not only boost user experience but also comply with accessibility standards that can help your website reach a broader audience.
Color Contrast and Font Choices
Clearly, the choice of colors and fonts plays a significant role in how easily your content can be read. It is important to maintain a high contrast between text and background colors to ensure visibility, particularly for individuals with low vision or color blindness. Websites that utilize dark text on a light background, or vice versa, typically offer the best readability. Additionally, you should opt for clean, sans-serif fonts that are simple and large enough to facilitate easy reading without straining the eyes.
Responsive Design for All Devices
There’s a growing necessity for websites to be functional across a variety of devices, from smartphones to tablets and desktop computers. A responsive design ensures that your site adapts to different screen sizes, allowing users to easily navigate and consume content regardless of how they access your site. Using flexible grids and images, along with CSS media queries, can significantly enhance the usability of your website for everyone, including users with vision impairments who may use screen magnifiers or other assistive technologies.
Font sizing should also be flexible and adjustable in responsive design. You can employ relative units like percentages or ems rather than fixed pixels to allow users to scale text as needed without compromising layout. By doing so, you accommodate a wider range of users with varying visual abilities, ensuring that your website is inclusive and functional for all.

Incorporating Accessibility into Your Content Strategy
Many organizations overlook the importance of accessibility in their content strategies, but it’s vital for reaching all users. A robust approach to accessibility not only helps you comply with legal standards but also enhances user experience and broadens your audience. By considering accessibility from the start, you can create content that is both engaging and navigable for everyone. For more tips on this subject, check out How to Improve Website Accessibility – 7 Helpful Tips.
Ongoing Training for Content Creators
One effective method of ensuring your content remains accessible is by providing ongoing training for your content creators. This training should cover accessibility guidelines, tools, and best practices to empower your team to create content that caters to all users. Keeping the lines of communication open about accessibility issues will foster a culture of awareness and consideration, making it easier for everyone involved to prioritize inclusivity in their work.
Building an Inclusive Brand
Your brand identity should reflect a commitment to inclusivity and accessibility. By actively integrating these values into your messaging, design, and outreach efforts, you can create a brand that resonates with a diverse audience. Moreover, by showcasing your dedication to accessibility, you can build trust with your users and encourage them to engage more with your brand.
The more you focus on building an inclusive brand, the more your audience will recognize and appreciate your efforts. This not only improves user satisfaction but also encourages loyalty and can even boost your brand’s reputation. As your audience grows, so does the impact of your accessibility initiatives, creating a positive feedback loop that enhances both your content and overall brand narrative.
To wrap up
From above, it is clear that adopting best practices in website accessibility is imperative for creating an inclusive online environment. You should integrate accessibility features into your design process, including alternative text for images, descriptive links, and proper heading structures.
Additionally, conducting regular assessments of your website can help you identify areas for improvement, ensuring that all users, regardless of their abilities, can navigate and interact with your content effectively.
Furthermore, educating your team about accessibility standards and guidelines will empower them to prioritize inclusivity in their work. By fostering a culture of accessibility within your organization, you can enhance the user experience for everyone and comply with legal standards.
Ultimately, investing in accessibility not only benefits those with disabilities but also improves your website’s overall usability and reach, which can significantly enhance your brand’s reputation and engagement in the long run.
Q: What are the key principles of web accessibility?
A: The key principles of web accessibility are often summarized by the acronym POUR: Perceivable, Operable, Understandable, and Robust. Perceivable means that information and user interface components must be presented in ways users can perceive. Operable indicates that users must be able to navigate and interact with the interface. Understandable implies that information must be clear and easy to comprehend, while robust means that content must be well-structured and perform reliably across different devices and assistive technologies.
Q: How can I test my website for accessibility issues?
A: To test your website for accessibility issues, you can use various tools and methods. Automated tools like WAVE, Axe, and Lighthouse can help identify common accessibility problems. However, it’s crucial to complement these tools with manual testing, which includes keyboard navigation, screen reader checks, and usability testing with real users, particularly those with disabilities. This combination will give a more accurate picture of your site’s accessibility.
Q: What are some simple changes I can make to improve accessibility on my website?
A: There are several straightforward changes you can implement to enhance accessibility on your website. These include adding alternative text for images, ensuring a good contrast ratio between text and background, using semantic HTML elements correctly, and providing clear navigational menus. Additionally, making sure that your site is navigable via keyboard alone and that form fields have associated labels can significantly improve user experience for individuals with disabilities.







